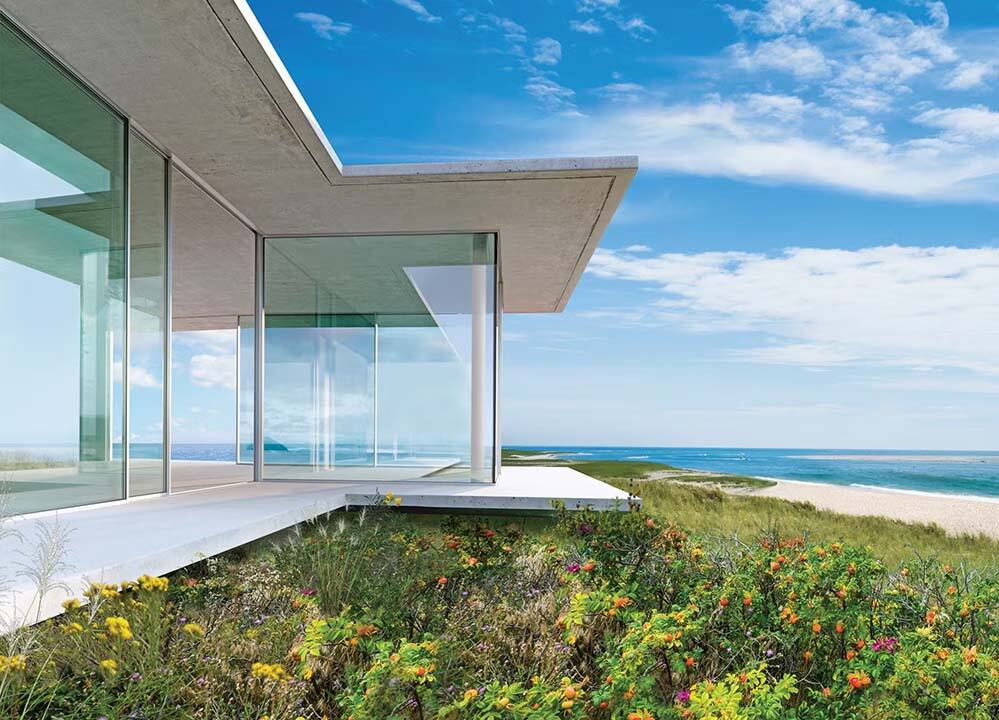
Understanding NFRC Ratings and Their Importance in Window Selection
What Are NFRC Ratings for Windows?
The National Fenestration Rating Council, known as NFRC, sets standard ways to measure how well windows, doors, and skylights perform when it comes to energy efficiency. Their system looks at several key factors including U-Factor which tells us about insulation quality, SHGC or Solar Heat Gain Coefficient that measures how much heat from sunlight gets through, VT for Visible Transmittance showing light passage, and AL meaning Air Leakage indicating how much air seeps through gaps. All products go through independent tests in lab settings so companies can't just guess their numbers. This creates a level playing field where consumers actually have reliable information to compare different products side by side without getting confused by marketing hype.
The Role of NFRC Certification and Labeling in Window Selection
When shopping for energy efficient products, NFRC certified labels act like quality stamps that show something has gone through rigorous testing procedures. The US Department of Energy backs this up when they say items with both ENERGY STAR and NFRC markings actually hit those government set efficiency targets. Having these two certifications together makes choosing products based on local weather conditions much easier. For instance, folks living in colder areas should look for windows with a U Factor number below 0.30 while residents in warmer climates would benefit more from products rated under 0.25 for Solar Heat Gain Coefficient. These numbers might seem technical but they really matter when trying to keep heating bills down during winter months or stay cool without breaking the bank on air conditioning costs.
How to Read NFRC Labels for Optimal Window Performance
Every NFRC label displays a product’s performance across the four key metrics. Homeowners should:
- Identify regional priorities (e.g., insulation vs. solar heat control)
- Compare values within the same product category (e.g., double-pane vs. triple-pane)
- Balance trade-offs (e.g., higher VT often correlates with slightly higher SHGC)
For cold climates, a U-Factor below 0.30 paired with an SHGC above 0.35 optimizes passive solar heating. In warm climates, prioritize SHGC below 0.25 to minimize cooling loads.
Key Components of the NFRC Label: U-Factor, SHGC, VT, and Air Leakage
| Metric | Ideal Range | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| U-Factor | 0.20–1.20 | Lower = Better insulation (reduces heat loss) |
| SHGC | 0–1 | Lower = Less solar heat gain (ideal for hot climates) |
| VT | 0–1 | Higher = More natural light (≈0.40 recommended) |
| Air Leakage | ≈≤0.3 CFM/ft² | Lower = Tighter seal (prevents drafts) |
Manufacturers achieving AL ≈≤0.3 cubic feet per minute per square foot (CFM/ft²) demonstrate superior construction quality.
Core Energy Performance Metrics: U-Factor and Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC)
Decoding the U-Factor: Measuring Thermal Insulation in Aluminium Windows
The U factor basically tells us how good a window is at stopping heat from moving through it. Lower numbers are better for insulation purposes, so anything below 0.30 counts as pretty decent performance. For houses located in colder regions, switching to windows rated at or under 0.30 can cut down on heating bills around 12 percent when compared against old fashioned single pane glass. These days manufacturers make thermally broken aluminum frames that hit U factors as low as 0.28 thanks to special polyamide strips between the metal parts plus clever multi chamber construction techniques inside the frame itself.
SHGC Ratings and Their Impact on Energy Efficiency in Different Climates
Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) measures solar radiation penetration, with optimal values varying by region:
- Hot climates: SHGC ≈≤0.25 minimizes cooling loads
-
Cold climates: SHGC ≈≥0.40 leverages passive solar heating
A 2024 analysis of sustainable facade designs found SHGC 0.35 ideal for temperate zones, balancing HVAC savings with natural lighting.
Balancing U-Factor and SHGC for Optimal Home Comfort
Energy Star recommends pairing U-factor 0.27–0.30 with SHGC 0.30–0.35 for mixed climates. This dual optimization prevents winter heat loss while mitigating summer overheating, maintaining year-round indoor temperatures within 68–75°F (20–24°C) in 84% of surveyed NFRC-rated installations.
Case Study: Energy Savings from Optimized U-Factor and SHGC in Residential Buildings
A Michigan housing development using aluminium windows (U-factor 0.29/SHGC 0.38) achieved:
| Metric | Improvement | Annual Savings |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Costs | 18% | $420 per unit |
| Cooling Demand | 22% | $310 per unit |
The $12,800 premium for NFRC-rated windows delivered full ROI through energy savings in 6.3 years.
Thermally Enhanced Aluminium Windows: Overcoming Conductivity Challenges for Higher NFRC Ratings
Thermal Conductivity of Aluminium Frames: A Performance Dilemma
Aluminium's inherent thermal conductivity historically limited its use in energy-efficient windows, with standard frames acting as thermal bridges that transfer 5x more heat than vinyl counterparts. This challenge created a persistent gap in meeting strict NFRC certification standards for thermal performance.
Thermally Broken Aluminium Designs Enhancing NFRC Compliance
The latest advances in thermal break tech have transformed how aluminum windows perform, mainly because manufacturers started putting polyamide strips between the inside and outside parts of the frame. According to what several top companies in the business are saying, this kind of innovation cuts down on heat movement through the frames by around 60-65% when compared with regular solid aluminum profiles. When paired with foam filled spaces inside the frame and double weather seals, these improved thermal frames can reach U-values as low as 0.28. That actually beats most wooden and vinyl options too, based on the latest numbers from the National Fenestration Rating Council back in 2023. For homeowners concerned about energy efficiency, this means significantly better insulation properties without sacrificing the structural advantages of aluminum frames.
Comparison of Window Frame Materials and Their Influence on Thermal Performance
When evaluated against common alternatives:
| Material | Avg U-Factor | Maintenance Needs | Lifespan (Years) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Aluminium | 1.20 | Low | 25–30 |
| Thermally Enhanced Aluminium | 0.30 | Low | 40+ |
| Vinyl | 0.35 | Moderate | 20–25 |
Thermally broken aluminium solutions now deliver superior longevity and equal or better insulation compared to premium vinyl systems, while maintaining inherent advantages in structural strength and design flexibility.
From NFRC Data to ENERGY STAR Qualification: Climate-Specific Certification Standards
How NFRC Energy Performance Ratings Support ENERGY STAR Certification
The NFRC energy ratings basically form the backbone of ENERGY STAR window certifications. Most manufacturers who get their products certified (around 92%) depend heavily on these NFRC tests when developing new windows. For a window to make the cut, it needs to hit certain performance targets related to things like heat loss (U-Factor) and solar heat gain (SHGC). These numbers have to match up pretty closely with what NFRC certifies as standard. The good news is that when they do align properly, homeowners can expect real savings on their heating and cooling bills. We're talking about potentially cutting down annual HVAC expenses by somewhere around 10-15% depending on how the windows are installed and where the house is located.
Regional Climate Zones and Their Impact on ENERGY STAR Window Requirements
ENERGY STAR divides the U.S. into three climate zones with distinct performance requirements:
| Climate Zone | Key Requirement | U-Factor Max | SHGC Max |
|---|---|---|---|
| Northern | Prioritize heat retention | ≈ ≤ 0.27 | No limit |
| Southern | Emphasize solar heat rejection | ≈ ≤ 0.40 | ≈ ≤ 0.25 |
| Coastal | Balance coastal storms & solar gain | ≈ ≤ 0.30 | ≈ ≤ 0.40 |
These regional standards ensure NFRC-rated windows meet localized energy challenges. For example, southern climates require SHGC values 38% lower than northern regions to mitigate cooling loads. Leading manufacturers now integrate climate-adaptive designs like thermally broken aluminum frames to satisfy zonal requirements while maintaining NFRC compliance.
Real-World Benefits of High-Performance NFRC Rated Aluminium Windows
Quantifying Energy Savings Through High-Performance NFRC Rated Windows
NFRC-rated aluminium windows with optimized U-factors below 0.30 can reduce heat transfer by up to 40% compared to standard models. When combined with low SHGC ratings (≈ ≤0.25), homeowners in cooling-dominated climates report 12–18% annual HVAC cost reductions.
Real-World Data: Reduction in HVAC Costs After Installing Top-Rated NFRC Windows
A three-year field study of 250 homes found that upgrading to NFRC-certified aluminium windows decreased annual heating and cooling expenses by an average of $440. Homes in extreme temperature regions achieved even higher savings–up to $740 annually–through strategic combinations of thermal breaks and low-E glazing.
Improved Indoor Comfort and Glare Control via Strategic SHGC and VT Optimization
By selecting windows with Visible Transmittance (VT) ratings between 0.40–0.60 and climate-appropriate SHGC values, homeowners maintain 72% of natural light while reducing solar heat gain by 33%. This balance minimizes glare on screens and helps maintain stable indoor temperatures within 2°F of thermostat settings.
Cost vs. Long-Term ROI of Premium NFRC-Certified Aluminium Windows
While NFRC-certified aluminium windows typically cost 15–20% more upfront than standard models, industry data shows a 7–10 year payback period through energy savings. Properties with certified windows also command 4–7% higher resale values, as validated by the National Association of Realtors' 2023 market analysis.
FAQ
What is the NFRC?
The National Fenestration Rating Council (NFRC) is an organization that sets standards to measure the energy efficiency of windows, doors, and skylights.
What do U-Factor and SHGC mean?
U-Factor measures insulation quality, while SHGC, or Solar Heat Gain Coefficient, indicates how much solar heat passes through a window.
Why are NFRC ratings important for window selection?
NFRC ratings provide reliable, standardized metrics that help consumers compare windows' energy efficiency without relying on marketing claims.
How do NFRC ratings impact energy savings?
Windows with optimized NFRC ratings can significantly reduce heating and cooling costs by improving insulation and minimizing solar heat gain.
Table of Contents
- Understanding NFRC Ratings and Their Importance in Window Selection
- Core Energy Performance Metrics: U-Factor and Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC)
- Thermally Enhanced Aluminium Windows: Overcoming Conductivity Challenges for Higher NFRC Ratings
- From NFRC Data to ENERGY STAR Qualification: Climate-Specific Certification Standards
- Real-World Benefits of High-Performance NFRC Rated Aluminium Windows
- FAQ
 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 LV
LV
 LT
LT
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 SL
SL
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 ET
ET
 HU
HU
 MT
MT
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 MS
MS
 GA
GA
 HY
HY
 UR
UR
 BN
BN
 GU
GU
 TA
TA